|
Frequently Asked
Questions
|
What is Plaque?
Plaque is the
accumulation of bacteria, microorganisms and their products which
sticks to the tooth surfaces. Dental plaque is soft and easily removed
by brushing and flossing the teeth. Accumulation of plaque can lead to
gum disease (gingivitis) and periodontal disease, as well as tooth
decay.
What is Calculus
(Tartar)?
Calculus is dental
plaque that has mineralized. Calculus can form when plaque is not
removed from the tooth surfaces. This plaque becomes old and
eventually forms into calculus. Calculus can form above or below the
gumline. The bacteria that sticks to calculus can cause gum disease
(gingivitis) or periodontal disease. Calculus cannot be removed by
brushing and flossing. A dental hygienist checks for calculus
formation when you visit the dental office. It is removed with special
instruments designed to adapt to the tooth surface affected without
causing trauma to the soft gums.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is
inflammation of the gums. Some common features associated with
gingivitis are red and swollen gums, and the presence of bleeding
while brushing and flossing. The cause of gingivitis is the bacteria
in dental plaque. This disease is reversible with good oral hygiene
practices.
What is Periodontal
Disease?
Periodontal disease
affects the periodontium (the supporting structures of the teeth). The
cause of this disease is multifactorial, but the presence of bacteria
in plaque certainly plays a major role. The supporting periodontal
structures begin to breakdown. This can mean that part of the bone
that supports the teeth or the ligaments that hold the teeth securely
in place are destroyed. This disease process is generally not
reversible and may require treatment from a dental professional
specializing in periodontal disease. Periodontal disease can develop
as a result of poor daily plaque control (e.g. brushing and flossing).
However, not everyone with poor brushing and flossing techniques will
develop this condition. It is wise to visit your dental hygienist or
dentist regularly in order to detect early stages of the disease and
to prevent further damage.
What is a Cavity?
A cavity is the
destruction of the tooth enamel, dentin, cementum and may involve the
tooth pulp.
How does a
Cavity Form?
The formation of a
cavity is due to many factors. For example, the tooth itself plays a
role (how strong it is); the mouths ability to cleanse itself (your
flow of saliva); diet (frequency and selection of sugary foods); the
bacteria in your mouth (good or bad); and the length of time the tooth
is under attack by the bacteria in your mouth.
Heredity:
may play a major role in how susceptible you are to the formation of a
cavity, for example:
- tooth structure,
size and shape of the tooth may be passed down through
generations. This includes deep pits and grooves which are ideal
"plaque traps", and therefore, are susceptible to decay
- there may be a
higher risk of cavities forming if your parents also had a large
number of cavities
- teeth that are
malpositioned in the mouth, that are hard to access with your
toothbrush or floss may also provide an ideal breeding ground for
the bacterial dental plaque.
- the absence of
fluoride during tooth formation and following tooth eruption can
increase the incidence of cavities. fluoride promotes strong tooth
development and remineralization of the tooth
Saliva:
has a protective function in the mouth, for example:
- a good flow of
saliva washes away food and bacteria that sit on the teeth and gum
tissues
- salivary flow
helps to neutralize the acids produced by bacteria from plaque,
thus a good flow helps reduce the chances of a cavity formation
Diet:
a well balanced diet from each of the four major food groups is
essential for your oral health, as well as, your overall health.
- avoid frequent
consumption of high sugar foods, especially sticky foods
- the longer the
time the food stays on your teeth, the greater the chance of
forming a cavity. If you do have a sugary snack, it's best to
brush your teeth soon after
- select between
meal snacks that are low in sugar concentrations such as white
milk, fresh fruits, raw vegetables, dark breads and whole grain
and enriched cereals
- sugar free
candies, gum and other snacks are an option
Time:
the actual amount of sugar eaten in one sitting is not as important as
when and how often you choose a sugar containing food.
- the consumption
of high sugar foods is best if eaten with a regular meal. This
will confine the sugar exposure to one sitting. It's best to eat
the whole chocolate bar at once instead of at different periods
throughout the day
Bacteria:
the mouth harbors many types of bacteria that are considered to be
normal in the human mouth.
-
bacteria, in a
healthy mouth tends to live in balance, but for reasons yet to be
truly identified, that balance can be tilted and oral disease may
result
Fluoride:
fluoride
provides many benefits. It is found in many products such as
toothpaste, mouthrinse, fluoridated drinking water and periodic
topical fluoride treatments applied by your dental professional.
- it aids in the
development of sound enamel
- it helps reduce
enamel solubility and increases enamel resistance to acid attack
- it prevents
demineralization (the white spot phase of the beginning stages of
a cavity)
- it enhances
remineralization of beginning stages of a cavity. Fluoride may
arrest further development of a cavity by depositing the fluoride
mineral called fluoroapatite
Fluoride used in
addition to daily brushing and flossing helps to reduce the chances of
a cavity.
Signs of a Cavity
Formation
The first sign of a
cavity forming may be a white spot, which in time may turn brown.
If it is a white spot,
low concentrations of fluoride applied frequently can arrest further
development.
White spot phase
If the white spot
phase progresses, further breakdown of enamel will occur. At this
point, a visit to your dental professional is necessary. The cavity
may be restored with a filling.
Good Habits to Help
Prevent Cavities
- regular visits
with your dental professional on an appointment schedule that
he/she recommends based on your own needs. Regular visits will
ensure you have the benefits of preventive care and early
diagnosis, as well as, treatment for any dental problems. Guidance
about home dental care can also be provided to avoid future
problems
- diet plays an
important role. Minimize the frequency of sugary foods, thus
reducing the amount of acid produced. Select snacks that are less
cavity causing, such as fresh fruit, plain yogurt and raw
vegetables
- the use of
fluoride will help decrease the risk of cavity formation
- good plaque
control. Maintain a strict and regular home care routine to
minimize plaque growth
it is
recommended that you consult your dental professional before using
any commercial products. You want to make a selection based on the
effectiveness of the product and your own personal needs.
Braces
Braces are put
on teeth to help correct rotated teeth, too large of spaces,
crowding or misalignment of teeth. Newer techniques today allow
for wire frames to be worn that can spread open the arch if it
is too small, or pull one side of the jaw to correct for overlap
on one side only. In addition, clear brackets and brackets that
can be bonded inside the teeth are making braces a good
option for many adults today.
Composites
Composite
or white plastic fillings, are used when esthetics is a concern.
While the currently available materials used for composites are
as strong as silver fillings on the chewing surfaces, they do
excellently in the grooves, and dramatically lower the
development of cavities.
Crowns
Crowns are
placed over a tooth when a large portion of the tooth is lost ot
decay or has broken off. Usually when a filling is more than
half of the size of the tooth, the tooth is weakened. If the
filling would comprise a significant portion of the tooth, often
the tooth can fracture under the stresses of chewing and
therefore, placing a crown over the tooth protects the chewing
surface and prevents that from happening. Crowns that are white
are made of porcelain and are usually placed in areas of
esthetic concern. Gold crowns might be placed in the molar
region or when there is heavy grinding that might damage the
opposing teeth.
Dentures
 Dentures
are false teeth. They are typically made from impressions
(molds) that are taken of the inside of the mouth and they are
made of a type of plastic or porcelain that duplicates the
shape, size and function of the teeth. Dentures
are false teeth. They are typically made from impressions
(molds) that are taken of the inside of the mouth and they are
made of a type of plastic or porcelain that duplicates the
shape, size and function of the teeth.
Implants
Dental
implants, simply put, are typically titanium posts that are
imbedded into the jawbone and then plastic or porcelain teeth
are placed over the portion of the implant that sticks out of
the gums. They usually take several months to complete since the
bone must fuse to the posts before any kind of pressure can be
put on the implant itself.
Nutrition and Dentistry
The more we learn about nutrition, the more that we believe that
a good diet will promote a healthier lifestyle and healthier
teeth. Especially if you are anticipating dental work, you might
wish to increase your Vitamin C, since it aids with healing.
During pregnancy, women should take extra care to eat right and
brush regularly since the hormone changes can affect the
susceptibility of the tissues to infection.
Root Canals
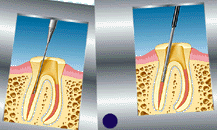
A root canal
is typically done whenever the decay or injury to the tooth
invades the inner part of the tooth where the pulp is. This is
where the nerve and the blood supply are located. When a root
canal is done, the inner portion of the pulp is removed, along
with any infection that may have invaded the inside walls of the
tooth. Then a sealer material is placed with a rubbery plastic
to fill the hole so that new infection can't get into the tooth.
Generally, by removing the root, it can potentially weaken a
tooth and therefore, it is common to protect the integrity of
the tooth by placing a crown over the tooth.
See also:
Root
Canal (Endodontic) Treatment
Sealants
Sealants used
to be considered for children's teeth only. Now we are finding
that adults too, can benefit from sealants. Sealants are plastic
coatings that are placed on the etched surface in the grooves of
teeth-typically on the back molars and sometimes on pre-molars.
It helps prevent sugars and bacteria from getting into those
deep fissures and cause decay.
Specialties of Dentistry
There are several recognized specialties of dentistry. Simply
stated, these are the specialties:
- Endodontics is the treatment
of root canals.
- Pedodontics is the
treatment of children.
- Periodontics is the treatment of the gums.
- Orthodontics is the
straightening of teeth.
- Oral Surgery is extracting teeth and jaw
surgery.
TMJ
The
temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) is a very unique and fragile
joint. Because of the numbers of tendons, ligaments and muscles
that are used to hold it in position, it is subject to trauma
and stress. As a result, headaches, jaw soreness and and
neckaches can all be related to problems related to the TMJ.
Sometimes the small disc that separates the lower jawbone from
the socket where it rests gets displaced and a bite splint may
be used among other therapies to "reposition" the jaw
into the proper alignment.
Toothbrushes
 Brushing
after each meal or snack is a great way to prevent cavities. If
your toothbrush is frayed at the ends, you should consider
replacing it. Let your toothbrush air-dry in between uses so you
don't get bacteria growing in it. Tap the water off and make
sure you don't leave food or toothpaste on the brush. Never
share a toothbrush with someone else and change it even more
frequently if you have been sick. Brushing
after each meal or snack is a great way to prevent cavities. If
your toothbrush is frayed at the ends, you should consider
replacing it. Let your toothbrush air-dry in between uses so you
don't get bacteria growing in it. Tap the water off and make
sure you don't leave food or toothpaste on the brush. Never
share a toothbrush with someone else and change it even more
frequently if you have been sick.
Do
you get headaches, especially in the morning?
Do they get worse when you are under a lot of stress?
You could be clenching and grinding your teeth while
asleep. There are different therapies that can free you from
this pain. The first step is to contact your dentist.
HELPFUL HINT:
Massage your jaw joint while in a hot shower.
Do
you eat sticky foods (like raisins) and drink lots of fruit
juice?
Although this sounds like a healthy snack, it may mean more
cavities. Raisins are high in sugar, and when they get stuck in
your teeth, there is a much higher incidence of cavity
formation. Fruit juice is also very high in sugar and constant
consumption can be a problem. Donít be afraid to enjoy these
foods and drinks; just enjoy them in moderation.
Seek
dental care immediately if you have:
Pain, non-healing sores, white/red growths in your
mouth, loose teeth, painful clicking in your jaw, frequent
headaches (especially in the morning), bleeding gums, or if you
havenít been to the dentist in more than six months.
What are cavities? How do they occur?
Cavities are a destruction of the tooth enamel. They
occur when foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and
starches) such as milk, pop, raisins, cakes or candy
are frequently left on the teeth. Bacteria that live
in the mouth thrive on these foods, producing acids as
a result. Over a period of time, these acids destroy
tooth enamel, resulting in cavities. This process is
also called "tooth decay."
I've smoked for many years and recently noticed a
white patch in my mouth should I be concerned?
Any mouth sore that persists for more than a week
should be examined by your dentist. Leukoplakia is a
thick, whitish-color patch that forms on the cheeks,
gums or tongue and is caused by excess cell growth. It
is common among tobacco users and can also result from
irritations such as ill-filling dentures or a habit of
chewing on one's cheek. The danger of leukoplakia is
that it can progress to cancer. Your dentist may want
to take a biopsy if the leukoplakia appears to be
threatening.
How can I help prevent oral cancer?
 Eliminate any risk factors such as tobacco and
alcohol and regularly visit your dentist. Periodic
dental exams allow early detection and appropriate
treatment if cancer develops. If at any time you
notice any changes in the appearance of your mouth or
any of these signs and symptoms, contact your dentist
at once: Eliminate any risk factors such as tobacco and
alcohol and regularly visit your dentist. Periodic
dental exams allow early detection and appropriate
treatment if cancer develops. If at any time you
notice any changes in the appearance of your mouth or
any of these signs and symptoms, contact your dentist
at once:
- A persistent sore or irritation that does not
heal
- Color changes such as the development of red
and/or white lesions
- Pain, tenderness or numbness anywhere in the
mouth or lips
- A lump, thickening, rough spot, crust or small
eroded area
- Difficulty in chewing, swallowing, speaking or
moving the jaw or tongue
- Change in bite
What's the difference between a canker sore and a
cold sore?
Canker sores are often confused with cold sores. An
easy way to distinguish between the two is to remember
that canker sores occur inside the mouth, and cold
sores usually occur outside the mouth.
A canker sore (also called aphthous ulcers) is a
small ulcer with a white or gray base and red border.
There can be one or a number of sores in the mouth.
Canker sores are very common and often recur.
A cold sore, which is also called fever blister or
herpes simplex, is composed of groups of painful,
fluid-filled blisters that often erupt around the lips
and sometime under the nose or under the chin. Cold
sores are usually caused by herpes virus type I and
are very contagious.
Canker sores usually heal in about a week or two.
Rinsing with anitmircobial mouthrinses may help reduce
the irritation. Over-the-counter topical anesthetics
can also provide relief. Cold sores usually heal in
about a week. Over-the-counter topical anesthetics can
provide temporary relief and prescription antiviral
drugs may reduce these kinds of viral infections.
Why did I get an abscess?
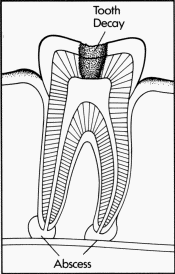 When the pulp of a tooth becomes infected (often
from a deep cavity or a deep crack), the infection can
spread throughout the pulp. If root canal treatment is
not done, the infection may travel into the tissues
near the root tip. This can cause the adjacent bone to
erode. The pocket of pus that forms is the abscess. If
the abscess increases in size, it can become more
painful. When the pulp of a tooth becomes infected (often
from a deep cavity or a deep crack), the infection can
spread throughout the pulp. If root canal treatment is
not done, the infection may travel into the tissues
near the root tip. This can cause the adjacent bone to
erode. The pocket of pus that forms is the abscess. If
the abscess increases in size, it can become more
painful.
See also:
Root
Canal (Endodontic) Treatment
|
![]()